With the release of the v2 of Microsoft Azure Backup Server (MABS) which supports Windows Server 2016, here is post to install and configure it – on Windows Server 2016 of course.
Azure Configuration
- Connect to your Azure tenant with a global administrator account to create a Recovery Vault
- Browse to reach the Recovery Services vaults section
- Then click Create Recovery Services Vault (if you have no recovery available), or Add to create a new one; I’m creating a new one
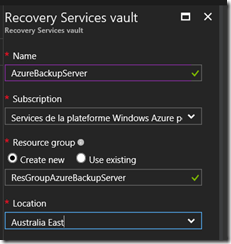
- Define the properties for the recovery vault (name, Azure subscription, resource group); even if I already have some resource group, I’m creating a new for this service
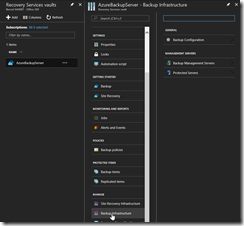
- Once created, you can change the storage replication options; by default this is set to geo-redundant. If you want to reduce the cost, you can switch to locally redundant. To change the configuration, open the recovery vault and access the Backup Infrastructure option and change the Backup Configuration
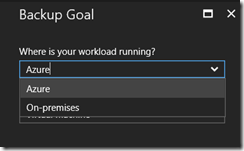
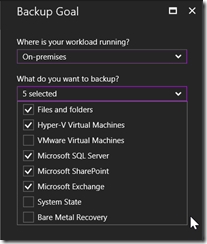
- Lastly,you have to download some component (including a vault credential). Go to the Backup section below the Getting Started and define the workload to On-premises as well as the type of workload you are going to backup
- Then you reach the Step 2 where you can download the Azure Backup Server agent (you can forget it as it will be done with the installation of MABS) and the vault credential; this is what you must download. NOTE the vault credential expires 2 days after you download it, if you don’t complete the setup within 2 days, you will have to download new credentials
- You are now done with this first step
MABS Installation
- Download all the files from https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=55269 and run the exe file to extract all the files
You have to use a dedicated server; no other workloads (especially AD, Exchange or System Center ones) must be executed on the server and if use Hyper-V (or VMWare) to host the MABS server do not use dynamic memory
- Then run the setup.exe
- Choose Microsoft Azure Backup Server – as I do not have Data Protection Manager (DMP) installed
- Follow the wizard to start the deployment, with first the prerequisites checking
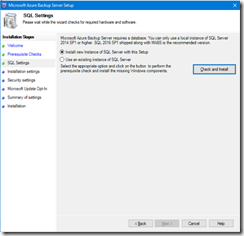
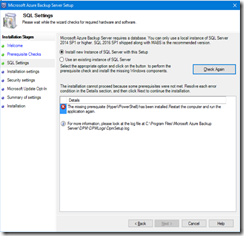
- If the checking result is good, continue to define the SQL settings; you have to install the SQL instance with the setup. This is quite disappointing you have an option to re use an existing SQL instance but this is not working
NOTE you may have to restart the server after checking the SQL instance because of some components have been installed
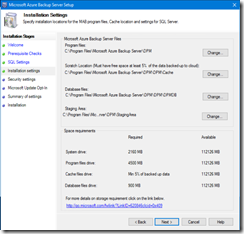
- Then you can define your installation settings – for the purpose of this post I kept all values as default
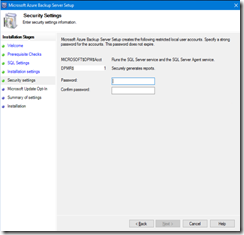
- Define a strong password to secure required local accounts; the account generating reports is reusing the serv
er name as logon name
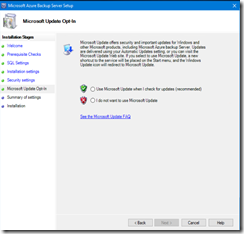
- Finally you define if you want to use WindowsUpdate for checking for update
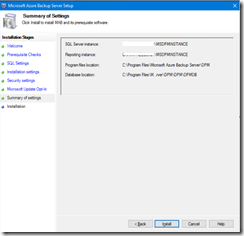
- At last the configuration summary before really starting the installation process
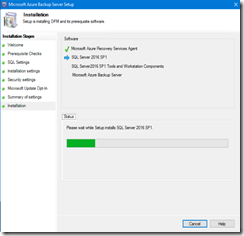
- During the installation, a new wizard will start to install the Azure Recovery agent; you usually have nothing to configure with this wizard, except maybe a proxy server and proxy account if it failed to connect to internet.
NOTE this wizard may be in the background
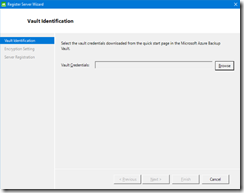
- Then a new wizard will appear to register the server with the Azure Backup vault; again it may be in the background
- You need to select the vault credentials downloaded after the vault creation
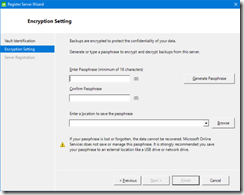
- Generate a passphrase and the location to save the passphrase; this will be used to encrypt/decrypt the backup
- Then the setup is completing the installation
The installation is now completed; you should have 2 new shortcuts in your desktop: one to launch Microsoft Azure Backup Server Management Shell and the other to launch the console Microsoft Azure Backup Server
Check network connectivity with Azure
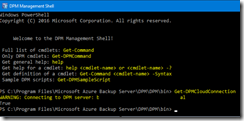
To ensure your Azure Backup Server has access to Azure to perform backup jobs, you can run the following PowerShell command
Get-DPMCloudConnection using the Azure Backup Server management shell
You must have as result True; meaning you have correct network connectivity.
Configure the backup of your workload
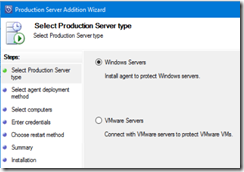
- Open the Microsoft Azure Backup server console and go to the Management section to add a new server to backup
- Select the server type between Windows and VMWare – for this post I’m adding a Windows server
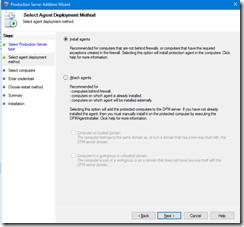
- Select the agent installation mode: install for servers within your corporate network (i.e. with no firewall) or attach for servers in your DMZ or other network with firewall between the backup server
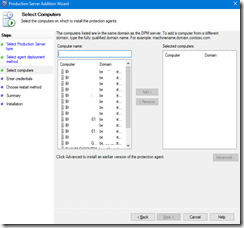
- You then have a prepopulated list of server (coming from your AD); you can also add server by typing manually the FQDN (useful for non domain joined server)
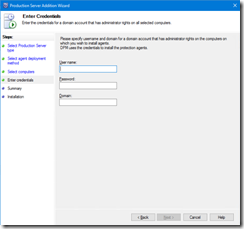
- Then you have to define a local admin account credentials; I would recommend to use a dedicated service account and grant local admin permissions
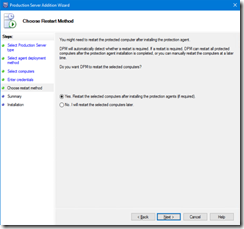
- You have to choose if you want to automatically restart the server after the installation of the agent
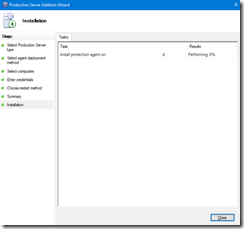
- Then the agent is installing
Configuration of the different options
Still using the Backup Server console you can configure multiple options from SMTP server for notification to self-service to allow end-user to restore their data.
- From the console, click on the Options button
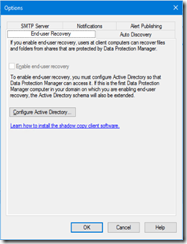
- Then you can configure end-user recovery, SMTP server and notifications, auto-discovery to automatically discover new client or SCOM integration
NOTE End-user recovery requires an AD Schema update. You can use the DPMADSchemaExtension.exe file (available in C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure Backup Server\DPM\DPM\End User Recovery) to extend the schema and delegate to a schema administrator.
You are now ready for using Azure Backup Server.